Among all trauma-related injuries worldwide, traumatic brain injury (TBI) is the leading cause of death and disability. Each year, an estimated 69 million people suffer from TBI, with low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) bearing the greatest burden [1]. Individuals in LMIC have more than twice the probability of dying after severe TBI when compared to patients in high income countries (HICs) [2]. Improvements in trauma care in LMICs could save an estimated 1 730 000 to 1 965 000 lives [3 ]. TBI clinical practice guidelines (CPGs) represent a lost-cost intervention which could improve in-hospital care in low-resource settings.
A major reason for improved TBI patient mortality rates and functioning outcomes in HIC hospital settings has been the widespread adoption of CPGs for acute TBI management [4]. CPGs shift the medical decision making from an individual’s judgement to evidence-based treatment, ultimately improving the consistency and quality of care provided. TBI CPGs institute a systematic approach to TBI treatment, focusing on prevention and early detection of secondary brain injury (such as from hypoxia and hypotension) and expediting definitive care. Evidence from middle-income countries (MICs) also supports the legitimacy of TBI CPGs as a strategy to improve patient outcomes [5 ,6]. Despite the growing support for TBI CPGs to improve care in HIC and some MICs, there remains little effort to investigate the potential for TBI CPGs to improve care in a low-income hospital setting [7,8 ].
The direct translation of a TBI CPG developed for a HIC to a low-income country (LIC) hospital presents challenges due to major differences between the emergency care settings [9 -11]. TBI CPGs developed in HIC settings require resources (ie, cervical collars, anti-seizure medications), specialized providers (ie, neurosurgeons), and technologies (ie, CT imaging and neurosurgical capabilities) that are not consistently available in LIC hospitals. When evaluating the applicability of standard CPGs used in the United States to a large teaching referral hospital in Rwanda, researchers concluded that implementation was not appropriate [12]. These findings underscore the importance of developing and adapting CPGs with local diagnostic, monitoring, and therapeutic capacities in mind. In addition, TBI CPGs may also provide added benefit in effective resource allocation for the low-resource setting [12].
To the best of our knowledge, the implementation of TBI CPGs has not been evaluated in a LIC. Given the burgeoning TBI burden in Sub-Saharan Africa, there is a critical need for cost-effective, easily scalable tools to optimize delivery of evidenced based TBI care [1,13]. As part of a quality care initiative, we collaborated with a zonal referral hospital in Tanzania to develop and implement TBI CPGs in the Emergency Department (ED). The aim of our study was to evaluate the impact of TBI CPG implementation on health care provider knowledge, attitudes, and practices, and assess the effect of implementation on TBI patient outcomes.
Study design
Our study included a pretest-posttest experimental design and an observational study component using a quasi-experimental design. The pretest-posttest portion examined the impact of TBI CPGs on hospital staff knowledge and attitudes using primary collected data. The quasi-experimental component assessed changes in hospital outcomes using time series analysis.
Ethical considerations
We received ethical approval from Kilimanjaro Christian Medical Center (KCMC) ethics review committee. The study was also found exempt by Duke University Institutional Review Board and Yale University Human Research Protection Program as a quality improvement project.
Setting
We conducted this study in the ED at the third largest hospital in the country, Kilimanjaro Christian Medical Center (KCMC) in Moshi, Tanzania. KCMC is a zonal referral center for the northwestern zone of Tanzania with a catchment of approximately 15 million people [14 ]. The hospital has a high burden of TBI, seeing an estimated 1000 TBI patients annually (approximately 6% of emergency visits [15]. The TBI mortality rate at KCMC is high at 47% for severe (Glasgow Coma Score (GCS)<9) TBI patients and 13% for moderate (GCS 9-13) TBI patients [15]. At the time of the study, total ED staff consisted of roughly 20 nurses, eight physicians, five to seven clinical officers or advanced medical officers, and two to five nursing assistants. The number of providers staffing the casualty department at any one time varied from two overnight to six during certain daytime hours. The department had access to basic laboratory services and radiological services (x-ray and computed tomography (CT)).
In 2013, KCMC established a prospectively collected TBI registry as part of a quality improvement effort [16]. The registry enrolled all acute (presenting <24 hours from injury) TBI patients presenting to the ED. The registry captured injury details, acute care, hospitalization care, and condition at discharge. Details regarding enrollment methods, inclusion and exclusion criteria have been previously described [15 ].
CPG Development and Implementation
After examining the current treatment standards and potential quality improvement areas, a multidisciplinary team created evidence-based and resource appropriate acute TBI treatment guidelines for the KCMC casualty department. The development of the guidelines was based on evidence-based trauma processes, the results of a systematic review of acute TBI management practice guidelines in high-, middle-, and low-resource settings, and the resource capacity at KCMC. See Appendix for full KCMC TBI CPGs. Implementation consisted of weekly educational training sessions with an emphasis on a standardized trauma process (ABCDE), identifying and addressing hypoxia, hypotension, and tachypnea, and using GCS to determine appropriateness of ICU admission, CT imaging and interventions such as seizure prophylaxis. Training sessions were held at the KCMC ED weekly for a total of 5 weeks to ensure all ED personnel participated in training. In addition, we installed posters displaying the CPG algorithm in the ED and distributed triage cards with CPG algorithm (including Glasgow Coma Scale calculation guide) to staff.
Data collection
Knowledge and attitude
We conducted a baseline assessment of emergency health care provider knowledge and attitudes towards the treatment and management of TBI patients. The customized survey tool included a 20-item multiple choice questionnaire modeled after a questionnaire created by researchers evaluating a TBI treatment “evidenced-based care bundle” (equivalent to CPGs) for ED nurses in Thailand [6] (Appendix S1 in the Online Supplementary Document ). The questionnaire was in English which is the language used at KCMC hospital in Tanzania. Since no language change was needed, we did not perform a formal question validation before implementation. However, to ensure the questions were understood and answered appropriately, we reviewed the questionnaire with our Tanzania research team at KCMC hospital. After their review and approval of appropriateness, we implemented the questionnaire.
The key areas of emergency TBI management knowledge assessed included: the use of the GCS for triaging and guiding patient management, airway management and cervical spine protection, ventilation management, circulation management, patient reassessment, patient positioning, diagnostic imaging, seizure prophylaxis, admission to the ICU, and pain management. One point was given for each correct answer, resulting in a total possible score of 20. The survey also included a 10-item Likert Scale questionnaire concerning health care provider attitudes towards their perceived competence and comfort with the treatment and management of TBI patients (Appendix S2 in the Online Supplementary Document ). The survey was administered in English and Swahili according to the fluency of individual KCMC staff. Prior to attending training sessions, staff completed pre-implementation assessments. The TBI CPG implementation and training took place in July of 2016. Post-implementation assessments were done two weeks after implementation.
Practice and hospital outcomes
To track change in practice, we harvested five clinical practice metrics from the TBI registry. We selected seven other demographic and clinical variables from the registry to assess change in outcomes. The data extraction ran from July 2014 to March 2017, starting 24 months prior to CPGs implementation and ending 9 months after. We included all patients enrolled during this period with complete data for the analysis. We excluded 61 patients with missing data.
The clinical practice metrics used to assess change in practice were: vital signs collected at ED presentation, IV fluids administered, CT scan performed, and oxygen given. For each patients, binary variables were created for hypoxia (<94% pulse oxygen), hypotension (<100 mm Hg systolic blood pressure), tachycardia (≥100 beats per minute) and tachypnea (>25 breaths per minute). We determined patient need for the five clinical practice metrics using the following protocol: a CT brain for patients presenting with a GCS<13 or if GCS>13, a CT brain if additional concerning factors present; fluids for hypotensive patients; and oxygen for patients who had hypoxia or a GCS<8. The low GCS requirement for oxygen was due to limitations in pulse oximetry and continuous pulse oximetry. Similarly, it is not standard at KCMC that TBI patients with a GCS of less than eight be intubated in the ED.
The demographic and clinical variables used to assess hospital outcomes were: age, gender, alcohol use prior to injury, TBI surgery performed, GCS, hospital disposition and Glasgow outcome score (GOS). The primary outcome variable was discharge GOS [17,18] ( Table 1 ). GOS ranges from one to five, each number representing a different level of recovery as described in Table 1 . We dichotomized this variable into good outcome (GOS of 5) and poor outcome (GOS of 1 to 4). We chose this cutoff, as compared to GOS of 4-5 representing good outcome, to improve the balance in the data set for the statistical analysis. About halfway through the data collection process, we switched from using GOS to using the Glasgow outcome scale extended (GOSe) to improve our descriptions of patients outcome disabilities. This scale ranges from one to eight. We converted those with a GOSe outcome to a GOS as shown in Table 1 . The registry did not include outcomes after discharge.
| Outcome | GOSe score | GOS score |
|---|---|---|
| Death | 1 | 1 |
| Persistent vegetative state | 2 | 2 |
| Severe disability | 3 or 4 | 3 |
| Moderate disability | 5 or 6 | 4 |
| Good recovery | 7 or 8 | 5 |
GOS – Glasgow outcome scale, GOSe – Glasgow outcome scale – extended
Data analysis
To assess the impact of the intervention, we conducted three sets of pre/post intervention statistical tests to test for significant changes in three areas: practitioner knowledge and attitudes, clinical practice, and patient outcomes. We used the R Language for Statistical Computing 3.4.1 for data management and statistical analyses [19].
Knowledge and attitude
We used Wilcoxon signed-rank tests to compare overall pre/post assessment scores and McNemar’s test to compare individual pre/post question scores. Wilcoxon and McNemar’s tests are nonparametric methods designed for paired data, and are appropriate given our small sample size and ordinal data [20].
Practice
We calculated descriptive statistics for the clinical practice metrics and compared the pre and post-intervention groups using t tests.
Hospital outcomes
In this study, randomization of the CPG implementation was not an option and we did not have treatment and control groups. Interrupted time-series (ITS) and difference in difference (DID) are two quasi-experimental approaches to evaluate an intervention effect using observational, longitudinal data [21].
An ITS is a useful method to estimate causal effect through regression modeling. We used both segmented regression models and Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) for the ITS. The segmented regression model [22] produces easy-to-interpret pre-intervention outcome trends, change in trends immediately after the intervention and post-intervention trends. While a segmented regression model can account for possible confounders, such as seasonality, an ARIMA model is a more robust technique for an ITS [23]. An ARIMA model can account for non-stationarity (baseline increasing or decreasing trends), seasonality, and autocorrelation (correlation of adjacent month data). The model output is the estimated monthly decrease in mortality after the intervention. For the ARIMA model, we performed the augmented Dickey-Fuller test to assess for stationary data. Two differences were needed to achieve stationary data (P < 0.01). Next, we compared Akaike’s Information Criterion (AIC) to identify the ARIMA model with the best fit.
We added the DID technique to strengthen our analysis of CPG intervention on outcomes. The DID leverages a historical control as a counterfactual. This counterfactual allows the test to obtain a causal effect using observational data. Additionally, this method can account for change due to factors other than intervention (ie, seasonality). We compared the difference in outcomes from the six months before (January-June 2016) and after (July-December 2016) the implementation to those same months of the previous year.
Participant characteristics
Of the 21 participants who completed the pre-intervention and post-intervention knowledge and attitude assessments, 85.7% were female and the median age was 40 years (interquartile range IQR = 24-66). The participants consisted of 12 nurses, three nurse assistants, three physicians, two advanced medical officers, and one medical student. The median number of years of post-primary school education was 7.5 years (IQR = 3-12) and the median number of years practicing was 12 years (IQR = 1-45). Seventy-one percent of subjects reported having treated more than 20 TBI patients in their careers, while 14% reported treating 6-20 and 14% reported treating 0-5.
Knowledge and attitude
Overall, there was a significant improvement in knowledge scores post-intervention (Wilcoxon signed-rank test, P < 0.001). For all but one question, the proportion of correct answers either stayed the same or increased, and McNemar’s test revealed that participants showed significant improvement in 6 out of 20 multiple choice questions. Specific areas that showed the largest improvements included questions pertaining to oxygen administration based on TBI category or oxygen saturation and CT scan criteria of mild TBI patients with GCS<15 (Table S1 in the Online Supplementary Document ). Overall, there was a trend towards a greater proportion of participants answering positively (“Agree” or “Strongly agree”) on Likert scale questions indicating comfort, competence or adequate training regarding the treatment and management of TBI patients, although none of these changes were significant (Table S2 in the Online Supplementary Document .
Practice
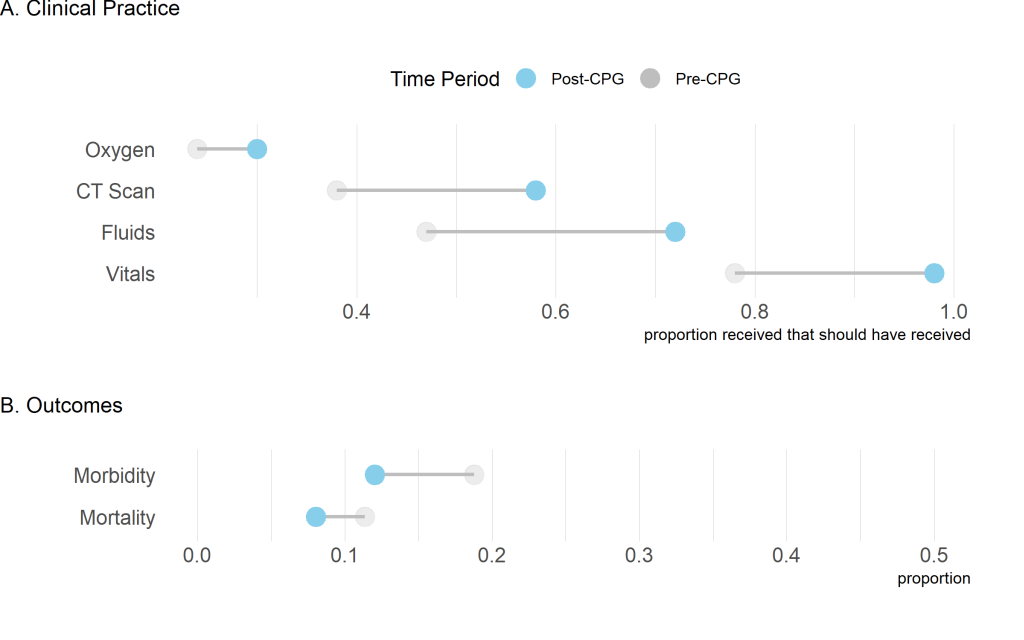
When comparing pre- and post-intervention provision of care, we found a significant improvement in CT scan administration, fluids given for hypotensive patients, and vitals collected ( Figure 1 ). There was an increase in administering oxygen to hypoxic patients, however, these findings were not significant ( Table 2 ).
| Proportion of those who received care practice metric if needed | t-test | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Care metric | Pre-intervention (July 2014-June 2016) | Post-intervention (July 2016-March 2017) | P-value |
| Oxygen | 0.24 | 0.30 | 0.327 |
| CT-scan† | 0.38 | 0.58 | 0.002 |
| Fluids | 0.47 | 0.72 | <0.001 |
| Vitals | 0.79 | 0.99 | <0.001 |
CT – computed tomography, CPG – clinical practice guideline
*Proportions were compared from before (July 2014-June 2016) and after (July 2016-March 2017) CPG implementation using a t test.
†No CT scanner data prior to August 2015 so data for pre-intervention is from Aug 2015-June 2016.
Hospital outcomes
Between July 2014 and March 2017, we enrolled 1886 TBI patients into the KCMC TBI registry. The majority of patients were males (N = 1561 [86%]) with a median age of 30 years (IQR = 21-41) ( Table 3 ). Of the 1886 TBI patients, 433 (23%) received a surgery intervention for their head injury. Alcohol was found positive in 482 (26%) of the patients. The mean admission GCS was 13.2 (SD = 3.3). From the ED, 1643 (88%) patients were sent to the surgical ward, 151 (8%) were sent home and 61 (3%) were sent to the ICU. Of the 1643 patients sent to the surgical ward, 243 (15%) were transferred to the ICU at some point during their inpatient stay. The average poor recovery rate for the duration of the study was 14.6%.
| Participants, N (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | Total | July 2014-June 2016, before-intervention | July 2016-March 2017, post-intervention | P-value |
| Clinical volume: | ||||
| TBI patients (per month) | 1886 (57.2) | 1438 (59.9) | 448 (49.8) | |
| Operations performed (per month) | 433 (13.1) | 317 (13.2) | 116 (12.9) | |
| Patient information: | ||||
| Adult (%) | 1561 (84) | 1172 (83) | 389 (88) | 0.023 |
| Pediatric (%) | 296 (16) | 241 (17) | 55 (12) | |
| Age median (25q-75q) | 30 (21-41) | 29.5 (21-41) | 30 (22-42) | |
| Male (%) | 1561 (84) | 1180 (82) | 381 (85) | 0.164 |
| Alcohol positive on admission | 482 (26) | 436 (31) | 46 (10) | <0.001 |
| Alcohol negative on admission | 844 (45) | 751 (53) | 93 (21) | |
| Alcohol unknown on admission | 542 (29) | 236 (17) | 306 (69) | |
| GCS mean (SD) | 13.2 (3.3) | 13.2 (3.3) | 13 (3.3) | |
| Disposition | 0.010 | |||
| ICU (%) | 61 (3) | 46 (3) | 15 (3) | |
| Surgical Ward | 1643 (88) | 1233 (86) | 410 (92) | |
| Home | 151 (8) | 130 (9) | 21 (5) | |
| Surgery to ICU | 243 (15) | 196 (16) | 47 (12) | |
| Outcome: | ||||
| Poor recovery (%) | 275 (14.6) | 221 (15.4) | 54 (12.1) | |
GCS – Glasgow coma scale, ICU – intensive care unit, TBI – traumatic brain injury, q – quartile
The pre-intervention group consisted of 1438 patients and the post intervention group consisted of 448 patients. Demographic and clinical characteristics were not significantly different before and after the intervention. Comparing the pre and post-intervention study groups, the poor recovery rate decreased from 15.4% to 12.1%. The average admission GCS scores were nearly identical at 13.2 pre-intervention and 13.0 post-intervention.
Interrupted time series
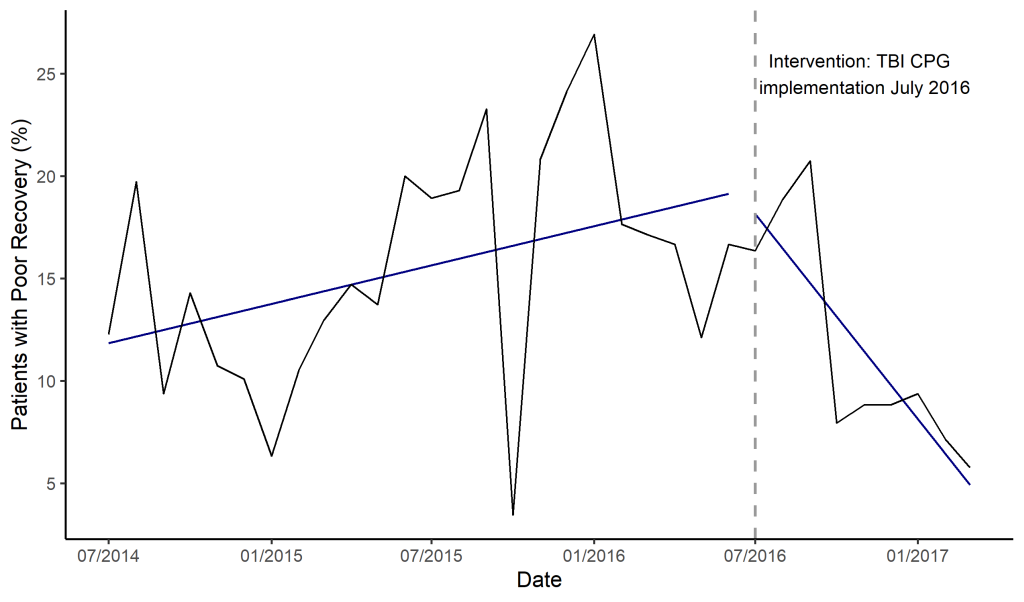
The segmented regression model revealed an increasing TBI poor recovery rate prior to implementing the intervention (P = 0.038) ( Figure 2 ). There was no significant increase or decrease in poor recoveries immediately after CPG implementation. In the months following the implementation, there was a significant decrease in poor recovery rate after the implementation (P -value = 0.005). The ARIMA supported the findings from the segmented regression with an estimated 1.7% decrease in poor outcomes per month after the CPG implementation ( Table 4 ).
| Model parameters | Segmented regression model | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Estimate (SE) | t | P-value | |
| Intercept | 0.1152 (0.0209) | 5.522 | <0.001 |
| Pre-implementation slope | 0.0032 (0.0002) | 2.176 | 0.038 |
| Change in slope | -0.0197 (0.0066) | -3.009 | 0.005 |
| Change in intercept | 0.0066 (0.0409) | 0.163 | 0.872 |
| ARIMA (1,1,1) × (1,1,1)12 model output | |||
| Intervention | -0.0165 | 0.0058 | – |
| Difference in difference analysis | |||
| Intercept | 0.1304 (0.0237) | 5.508 | <0.001 |
| Time | 0.0528 (0.0335) | 1.576 | 0.131 |
| Treatment | 0.0482 (0.0335) | 1.439 | 0.166 |
| DID estimate | -0.0955 (0.0474) | -2.017 | 0.057 |
ARIMA – Auto Regressive Integrated Moving Average, DID – difference in differences
Difference in difference (DiD)
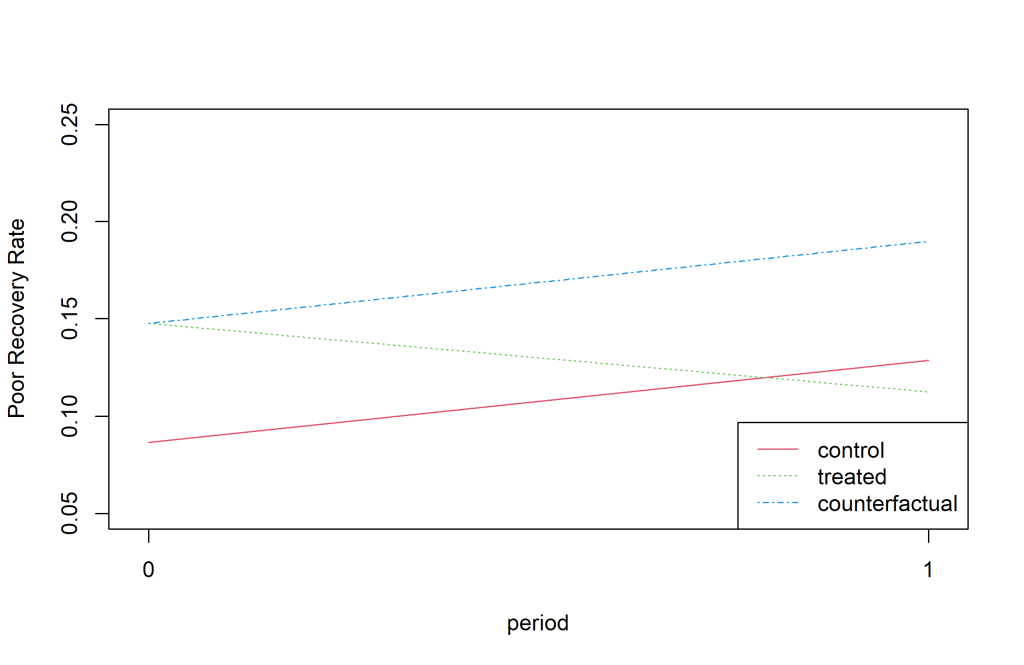
The difference in difference estimate was negative (-0.0955) indicating a larger decrease in the poor outcome rate between July-December 2016 and Jan-June 2016 compared to the difference between July-December 2015 and Jan-June 2015 ( Figure 3 ). The findings were nearly significant with a P-value of 0.057.
To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first implementation and evaluation of locally adapted CPGs for acute TBI management in a low-income country. We evaluated the implementation using five clinical practice metrics and outcome data from a prospectively collected TBI registry. Following implementation, we observed significant increases in three of the clinical practice metrics: collection of vital signs, the ordering of CT scans when indicated, and IV fluid administration when indicated. A significant change was not observed in the use of supplemental oxygen when indicated. Most importantly, our CPG implementation corresponded with improvements in hospital outcomes. Overall, this study provides a comprehensive evaluation of a TBI CPG implementation on provider knowledge, attitudes, practice, and hospital outcomes in a low-resource setting.
Changed practice metrics
Following CPGs implementation, we observed increases in collection of vital signs, the ordering of CT scan when indicated, and IV fluid administration when indicated. An increase in these practices could be due to CPGs implementation training, a finding supported by research from high- and middle-income countries. The significant improvement in practice metrics corresponded to statistically significant increases in post-assessment knowledge scores, strengthening our confidence in the causality of these changes in practice. We are cautious to ascribe our findings directly to the intervention, as additional factors related to resource availability common to low-resource settings may have influenced observed improvements. For example, the KCMC CT scanner was under maintenance for periods throughout our study but the frequency of those non-operational days before and after CPGs implementation was unknown.
Additionally, the CT scan cost per patient is relatively high ($250 000 Tz Shillings or US$125) and concerns regarding this cost burden may been communicated from patients and families to providers, influencing decision making regarding CT scan utilization. Fluctuations in the availability of IV fluids, Spo2 monitors, blood pressure monitors, and staff may also have influenced changes in practice metrics. Changes in ED leadership, staff incentives, and staff training outside of our CPGs implementation may also have influenced practice changes. While vital sign recording improved significantly after CPGs implementation, vital sign recording was high (79% of patients) and appeared to be on an upward trend prior to CPGs implementation based on our time series analysis. Of note, this vital sign completion percentage was already higher than reports from similar settings prior to CPG implementation.
Unchanged practice metrics
Following CPGs implementation, the use of supplementary oxygen did not significantly change. We suspect failure to see an improvement in supplemental oxygen is largely reflective of resource constraints rather than provider’s knowledge for two reasons. First, we found the greatest improvement on the post assessment knowledge scores in this area. Second, at the time of the study, oxygen supplies were not always available and oxygen access points were not readily accessible in the KCMC ED. The limited availability of oxygen in emergency care settings and poor oxygen administration when indicated are consistent with other studies in the region [24,25].
Outcomes
In spite of implementing a time-limited educational intervention, we observed marked improvements in patient outcomes. The poor outcome rate steadily increased in the pre-implementation period. Over the nine months following implementation, the poor outcome rate decreased at an estimated 1.6% each month. To help account for possible spurious findings and mitigate the strong seasonality of these data, we performed two different models (segmented regression and ARIMA) using two different longitudinal data analysis techniques (ITS and DID). Our findings of a CPG implementation improving outcomes are consistent with similar efforts in Columbia, India, Pakistan, and Thailand [26-28]. However, findings from similar hospital settings in Rwanda, Kenya, and Malawi show that ability to standardize care is heavily influenced by additional factors such as resource availability, functioning equipment, and prohibitive costs, which may also have been the case in our study [12,29]. Provided that additional, uncontrollable factors can influence standardization of care, and that our study included one hospital, we must acknowledge the context specific nature of our findings.
Limitations
There were several limitations to this study. First, this study focused on one zonal referral hospital in Tanzania which may reduce the generalizability of our findings. We did not implement the CPG guidelines at multiple hospitals and did not include another hospital as a control. To mitigate the lack of a control, we used multiple analytical techniques including historical controls and controlling for seasonal and other temporal trends. Also, by focusing on one hospital, we were able to develop a rigorous implementation from which we can now expand to other centers. An additional major limitation when assessing practice changes is the possible overlap of access challenges. For example, we did not capture dates when the CT scanner was broken or under maintenance. Hospital and patient resource constraints are other expected limitations given the study settings. Additionally, the hospital’s limited supplies or patients who are unable to afford treatments could negatively bias our findings. In analyzing outcomes, we observed strong seasonality. There was an annual decrease in poor recovery rate during early fall and an increase during winter. One possible explanation for the increased mortality during winter is that November marks the start of the school year for interns and residents. This period is when the student doctors have the least experience. We used an ARIMA model and DID technique to mitigate the observed seasonality. We also did not directly observe provider practice. We inferred change in practice based on what was recorded in the registry. Other limitations which could increase or decrease our observed findings include resource shortages, power outages, and cost-prohibitive metrics (eg, CT scans).
In this study, we have shown that locally relevant TBI CPGs can be developed, implemented and result in significant improvements in TBI care in a low resource setting. We believe further research is needed on the causal effect of CPGs on TBI outcomes. Additionally, future research should assess the longevity of CPG implementation training on clinical practice and outcomes. Given the great and growing TBI burden in LMICs, low cost, highly scalable solutions like TBI CPGs represent a major opportunity to reduce undue morbidity and mortality.